I’m attending the KLA-MLA joint conference this week in Kansas City. Any blog posts, please be forgiving of spelling/grammar mistakes, as I’m live blogging.Â
Sarah Sutton, ESU;Â Mary Bailey, K-State;Â Christina Geuther, K-State;Â Nancy Haag, KCKPL;Â Erich Kessler, KCKPL;Â Angela Rathmel, KU
1. Introduction to the NASIG Core Competencies for Electronic Resources Librarians – Sarah Sutton
When looking at the competencies, there’s no way to be competent in all of the competencies. Don’t be overwhelmed by all the competencies and what they’re asking for…
#1: The life cycle of electronic resources. The ERL has extensive knowledge of the concepts and issues related to the lifecycle of recorded knowledge….
#2 Technology. Providing and maintaining accessing to electronic resources is a primary responsibility of ERLS. IT requires theoretical and practical knowledge of the structures, hardware, and software underlying the provision of access to electronic resources, and their interrelatedness….More competent than average in technology
#3Â Research and Assessment, which includes data generated by e-resources; collect/analyze/manipulate/interpret data; research methods; evaluate products and services; problem solver
#4 Effective communication, which includes communicated with a broad range of internal and external stakeholders; synthesizing complex and ambiguous phenomena; working collaboratively; frame situations from others’ perspectives; use data to make persuasive arguments must be able to talk to IT; regular users; and everyone in between
#5 Supervising and Management, which includes effectively supervise, train and motivate staff; project management; evaluate existing procedures and workflows; create policies and best practices for e-resource management; establish and maintain effective working relationships; familiar with systems administration…..show IT you want to learn
#6 Trends and professional development, The ERL works with concepts and methods that are very much in flux, and so has an abiding commitment to ongoing professional development thru CE, attendance at prof conferences, webinars, following related professional lit, blogs, listservs, and other learning venues. This is especially important due the fast-paced change nature of eresources.
resources list
- Serials Listserv
- Eril-l listserv
- NASIGÂ (prof org) — NASIG list, newsletter, blog posts, workshops, webinars, and conference
- UKSGÂ (prof org)Â — newsletter, blog posts, workshops, webinars, and conference
- ALCTS eforums list
- National Public Radio Twitter: @npr
- Scholarly Kitchen Twitter: @scholarlykitchen
- Ars Technica Twitter: @arstechnica
- Wired magazine Twitter: @Wired
- ILS listserv
- Twitter — esp at professional conferences
- Library as Incubator Project Twitter: @IArtLibraries — lots of eresources-related projects highlighted on their site
#7 Personal qualities. The ERL demonstrates: flexibility, open-mindedness and the ability to function in a dynamic, rapidly changing environment; a high level of tolerance for complexity and ambiguity; unrelenting customer service focus and dogged persistence in the services of users; skillful time management. Being kind and compassionate with all users
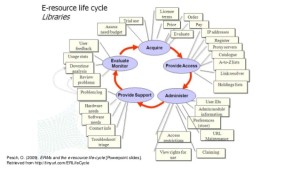
2. The E-Resources Life-Cycle –Â Sarah Sutton
There’s no beginning or end — Acquire, Provide Access, Administer, Provide Support, Evaluate, Monitor
Link Resolvers — behind the scenes for the result in one database and the full-text link in another database
3. Technology for E-Resources
KCKPL EResources –Â Nancy Haag
KCKPL was seeing that eresources usage was going down.
Digital User: access to materials via personal devices; instantaneous access to materials; constantly want new material
Digital Platforms in use: Hoopla; OneClick Digital; Axis 360: Tumblebooks; Databases; Zinio; Yearbooks — simultaneous access
Road block for Digital User: Getting a library card — instead, shift to right here, right now. Simple registration
eCard online user registration: Only validation: zip code; no additional validation to active the card; shorter library card number (6 not 14 digits); no physical library card [no fines are fees]. Didn’t even require confirmation email
ecommunity.kckpl.org — focused around the themes of lifelong reading; life-start reference; community-life entertainment
EResource Central — vendor project from Sirsi — one sign-on
Hoopla in beta for a single sign-on
Is this working? user registration and stats have increased. Re-evaluated way things have been done and designed, looking at stats. Will be designing a single screen, with a simple reader’s advisory piece. Initiative has been very useful and positive.
4. K-State Univeristy E-Resources –Â Christina Geuther
$5.8 million budget for electronic resources; 21,581 FTE in 2014 (determines contracts); Ex Libris Verde to Ex Libris Alma
Staffing Department: Head, Content Dev/acquisitions; content development librarians; continuing resources librarian; electronic resources librarian (documenting licenses & license alternatives; modules); electronic resources access specialist; interlibrary loan services
- proxy server — off-site credentialed access; EZProxy is a commonly used one
- link resolver — connecting databases, moving from a source to a target; OpenURL standard
- electronic resource management system (ERM) — holds license material; usage stats; acquisitions record; works on a schedule
- discovery layer — multiple db and library catalog — central index; Ex Libris Primo product used at K-State; can be interfaced at ILL; walkin use if proxy server can’t be used, etc.
5. Wrangling Data Generated by E-Resources –Â Erich Kessler
Lots of data — interconnected & instinct — more I understood data, the less scary it was
Usage stats; error logs; userids; timestamp; and so much more
Vendor relationships — vendor websites; proprietary products (can help aggregating data — doesn’t have to be manual); vendor support. Asking for help, to interpret data; the vendors want you to understand data, bc they want your business. Ask for help as you get started. Ask questions!
Making sense of the data — collect; analyze; manipulate; meaningful interpretation; methods (relational dbs; spreadsheets; word processing programs)
Assessment — examine, evaluate, objectivity, needs of the users, subscription (terms)
Research methods — specifications, efficacy, and cost efficiency; bibliometrics (collection assessment); systems analysis (troubleshooting)
Principles & techniques — id’ing and analyzing; emerging technologies; innovations; recognize & implement improvements
Wrangling Data: reporting — usage & cost per use; needs & budget constraints (when to recommend cancellations; when to add); reports — strengths & weaknesses
Publisher & vendor pricing policies — package deals & alternatives
Behind the scenes skills: problem solving; organization (mixing data sets = bad); analytical; detail-oriented
6. Communicating effectively with e-resources stakeholders from IT specialists to technophobic patrons –Â Angie Rathmel
Biggest part of communication — relationships
Angie — Ambivert; Not always great at it; grew better thru music, teaching, psychology; influenced professionally: strengths & vulnerability, Dervin; Everyone his/her e-resource
NASIG competency 4.4 – Demonstrating the ability to work collaboratively with other units and staff, establishing and maintaining effective working relationships. “If you want to go fast, go alone; if you want to go far, go together” –African proverb
Messaging and empathyÂ
- 4.1– effective; promptly; consistent; verbal/written; teamwork –Â tailor the message to the circumstances and to the audience as needed
- 4.5 — see situation from others’ perspectives
Empathy — How? active listening; join committees; smile, small talk; reference desk shifts; regular meetings [seeing how people outside your work are influenced by your work]
Less is moreÂ
4.2 — synthesizing into easy to understand summaries of complex and ambiguous phenomena; figuring out what details to leave out;
Empathy, again; terminology, jargon; questioning (reference interview) “Tell me more about that….”; start small (IM is nice for starting small); don’t bury lead, esp when emailing
Just the facts, ma’am…
4.3 — explaining and instructing clearly and concisely, when and as needed; rises above personal feelings and frustrations in order to provide the best possible services and resources to end users;
comes down to information management — balance between communicating by talking and reaching out vs controlling flow of information to what’s most effective
Information Management — How to separate wheat from chaff
- Improve email (personal task tracking, shared accounts)
- Web forms
- Ticketing systems
- Spotlights vs Lobs (Feather, 2007) — highlight spotlights (common problems); eliminate the lobs, the back and forth communication
Other How?Â
- Emotional intelligence (for you), empathy (for others)
- Strengths
- Facilitation, project management
- Practice, practice, practice
- Brene Brown on Empathy video short
Resources
- Facilitation at a glance
- Rising strong
- Daring greatly
- Go put your strengths to work
- Sense-making methodology reader
- Electronic Resources Communications Management: A Strategy for Success
- Tools, Techniques, and Training: Results of an E-Resources Troubleshooting Survey
7. Effective Management of E-Resources Personnel and Projects –Â Mary Bailey
Effectively supervise, train and motivate staff
- Know your staff
- What motivates them
- What is their learning style
- Trust them to do their job
- Praise and reward them <– Important!Â
- Help staff improve weaknesses and build on strengths
- Listen to them
- Can they multitask? Do they need goals? Deadlines?
- You learn your staff, and then you work with them in their style, and then you trust them to do their job.
Project management
- timeline and deadlines — then break into pieces
- gather the right group of stakeholders
- take the time for planning, lots of time
- Do first yourself –> Then Document
- Training
- Evaluate and re-evaluate
- Motivate and reward
I left during this section
8. Personal Qualities Demonstrated by Those Who Excel at Functioning in the Dynamic, Rapidly Changing Environment of E-Resources –Â Panel discussion
I left beforee this section